다발경화증과 유사하게 발현한 동종 조혈모세포이식 후 중추신경계 이식편대숙주반응
Central Nervous System Graft-Versus-Host Disease Mimicking Multiple Sclerosis after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Article information
J Mult Scler Neuroimmunol. 2023;14(2):137-138
aDepartment of Neurology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
bDepartment of Neurology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
cDepartment of Neurology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
a인제대학교 부산백병원 신경과
b인제대학교 해운대백병원 신경과
c경희대학교병원 신경과
Address for correspondence: Seong-il Oh, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, 23 Kyungheedae-ro, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 02447, Korea Tel: +82-2-958-8499, Fax: +82-2-958-8490 E-mail:
seongil.oh@gmail.com
Received 2023 July 5; Revised 2023 August 4; Accepted 2023 August 24.
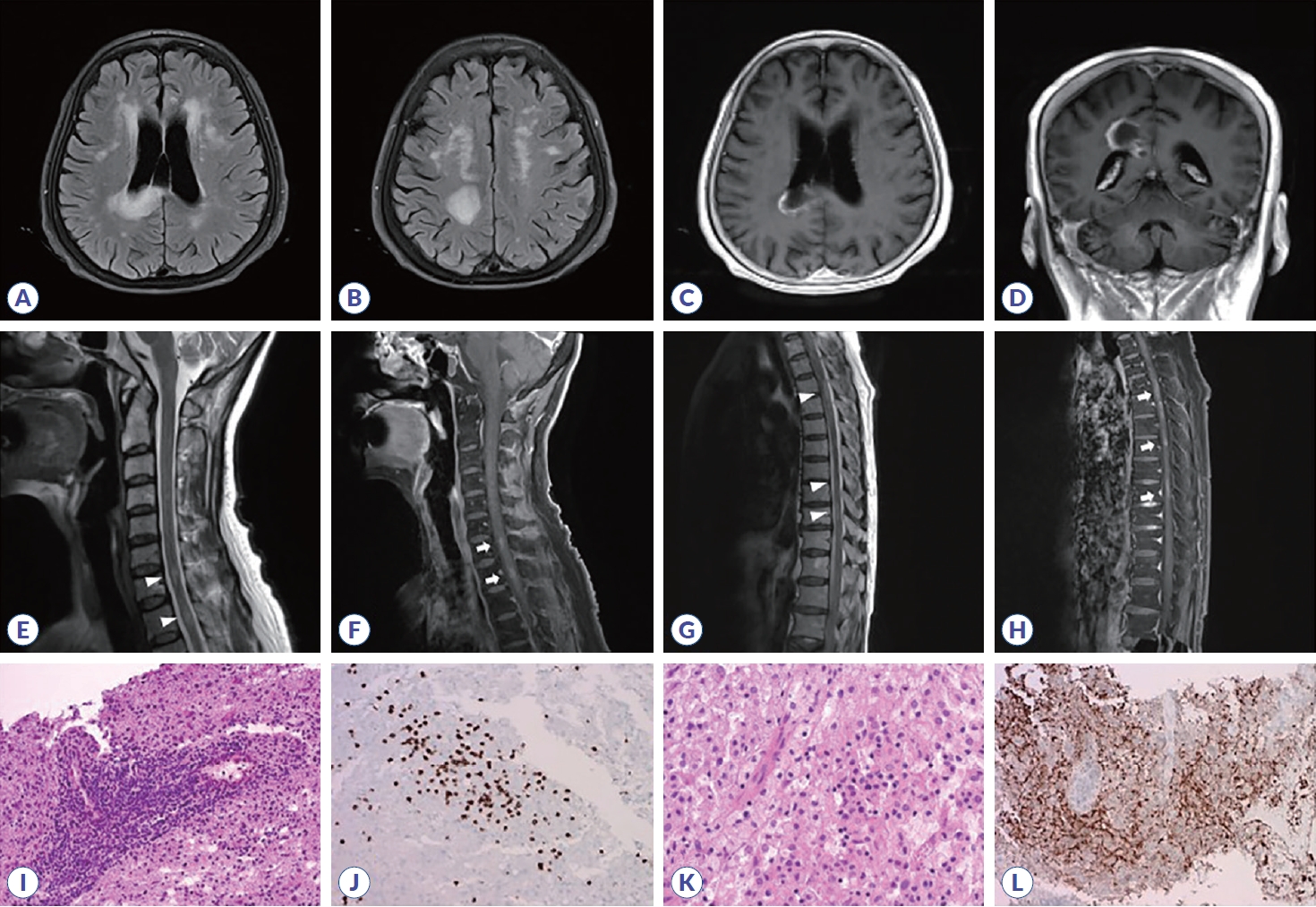
A 64-year-old female underwent salvage chemotherapy followed by allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloHSCT). At 18 months after alloHSCT, she developed dysarthria and gait disturbances. Brain MRI revealed multifocal lesions with enhancement (). A brain biopsy near the right callosal splenium showed patchy demyelination and T-cell infiltration (). Spine MRI revealed multiple short-segment myelitis with enhancement (). Since central nervous system (CNS) graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after alloHSCT can lead to severe neurological complications, further research is needed to elucidate the risk factors of CNS GVHD and to manage it appropriately.1,2
Initial brain and spine MRI (A-H) and pathologic findings of corpus callosum biopsy (I-L). (A-D) Initial brain MRI showed markedly increased extent of multifocal patchy and confluent T2/fluid-attenuated inversion recovery hyperintense lesions with heterogeneous enhancement at the right parietal lobe and corpus callosum. (E, F) Spine MRI showed multiple T2 hyperintense lesions (C6-7 and T1 segments, arrowheads) with nodular enhancement (arrows). (G, H) Multiple eccentric short-segment thoracic spinal lesions (T4-T5/6, T6/7 and T9-10 segments, arrowheads) with multifocal enhancing lesions (arrows) were also observed. (I) Infiltration of some cytotoxic T-lymphocytes was observed, especially in a perivascular cuffing pattern, on frozen section (Hematoxylin and Eosin [H&E] staining, ×100). (J) Lymphocytes were stained with CD8 immunohistochemical stain (×200). (K) Most parenchyma was filled with many foamy macrophages and some lymphocytes (H&E, ×200). (L) Staining for myelin basic protein (MBP), suggesting myelin phagocytosis, is patchy within the lesion, indicative of diffuse demyelination (MBP immunohistochemical stain, ×100).
References
1. Grauer O, Wolff D, Bertz H, Greinix H, Kühl JS, Lawitschka A, et al. Neurological manifestations of chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: report from the Consensus Conference on Clinical Practice in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Brain 2010;133:2852–2865.
2. Buxbaum NP, Pavletic SZ. Autoimmunity following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Front Immunol 2020;11:2017.
Article information Continued
Copyright © 2023 by Korean Society of Neuroimmunology
Figure 1.
Initial brain and spine MRI (A-H) and pathologic findings of corpus callosum biopsy (I-L). (A-D) Initial brain MRI showed markedly increased extent of multifocal patchy and confluent T2/fluid-attenuated inversion recovery hyperintense lesions with heterogeneous enhancement at the right parietal lobe and corpus callosum. (E, F) Spine MRI showed multiple T2 hyperintense lesions (C6-7 and T1 segments, arrowheads) with nodular enhancement (arrows). (G, H) Multiple eccentric short-segment thoracic spinal lesions (T4-T5/6, T6/7 and T9-10 segments, arrowheads) with multifocal enhancing lesions (arrows) were also observed. (I) Infiltration of some cytotoxic T-lymphocytes was observed, especially in a perivascular cuffing pattern, on frozen section (Hematoxylin and Eosin [H&E] staining, ×100). (J) Lymphocytes were stained with CD8 immunohistochemical stain (×200). (K) Most parenchyma was filled with many foamy macrophages and some lymphocytes (H&E, ×200). (L) Staining for myelin basic protein (MBP), suggesting myelin phagocytosis, is patchy within the lesion, indicative of diffuse demyelination (MBP immunohistochemical stain, ×100).