대뇌 실질을 침범한 IgG4연관비후경수막염
An Immunoglobulin G4-Related Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis Involving Cerebral Parenchyma
Article information
특이 과거력 없는 56세 남자가 두통 및 처음 발생한 경련으로 방문하였다. 두통 이외에 다른 신경학적 이상 소견은 관찰되지 않았으며, immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) 수치가 98 mg/dL (정상범위, 3.9-86.4 mg/dL)로 증가되어 있었다. 뇌 자기공명영상상 왼쪽 두정엽에서 덩이 모양의 결절성(nodular) 경막 비후가 뇌실질 침범과 함께 관찰되었으며, 왼쪽 대뇌반구 전반에 걸쳐 미만성(diffuse) 경막 비후 소견을 보였다(Fig. 1). 정확한 감별진단을 위해 시행한 조직생검에서 다수의 림프구 침윤이 동반된 섬유화와 많은 IgG4 양성형질 세포(95/high power field)를 확인함으로써 IgG4연관비후경수막염으로 진단하였다. 이후, methotrexate 10 mg/week와 경구 스테로이드(prednisolone 10 mg, every other day)를 3년째 투여 중이며, 증상 및 영상학적 소견(매년 추적 검사를 시행) 모두 호전된 상태이다. IgG4연관비후경수막염은 경막 비후를 특징으로 하나, 드물게 뇌실질 침범과 함께 경련이나 신경학적 이상 소견을 유발하므로 이에 대한 고려를 필요로 한다.1,2
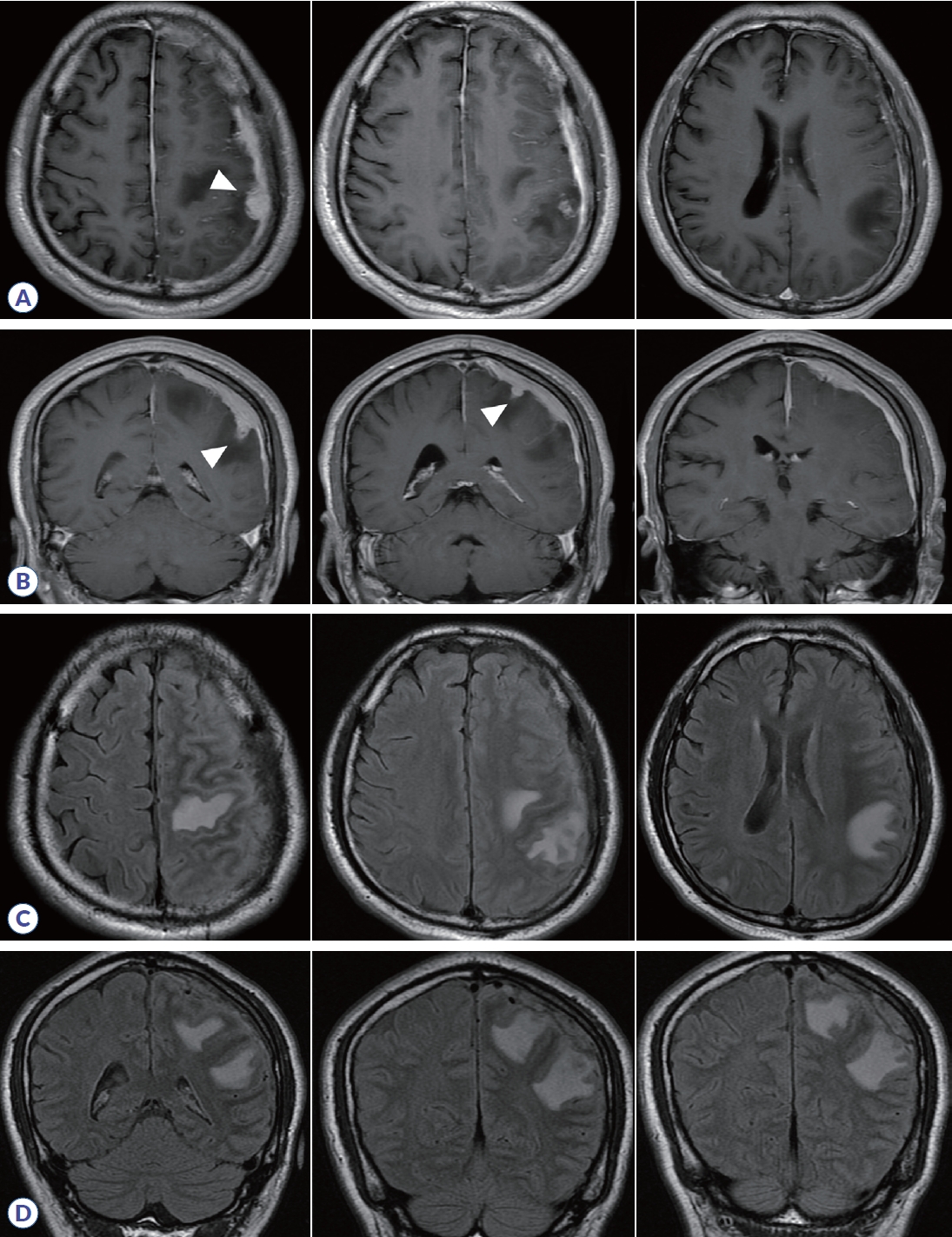
Brain MRI of patient. Axial (A) and coronal (B) T1 gadolinium-enhanced images showed diffuse dural thickening on left hemisphere and nodular enhancing lesions (arrowheads). FLAIR-hyperintense lesions were observed in the left hemisphere, suggesting the involvement of cerebral parenchyma (C, D). FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery.
Notes
Conflict of Interest
Kim KH, and Hyun JW reports no disclosures. Kim SH received a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea and National Cancer Center; consulted and received honoraria from Bayer Schering Pharma, Merck Serono, Eisai, Teva-Handok, Celltrion, and Roche. Kim HJ received a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea and research support from AprilBio, Eisai and UCB; received consultancy/speaker fees from Alexion, Altos Biologics, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Daewoong Pharmaceutical, Eisai, GC Pharma, Handok Pharmaceutical, Kaigene, Kolon Life Science, MDimune, Merck Serono, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Roche, and Sanofi Genzyme; is a co-editor for the Multiple Sclerosis Journal and an associated editor for the Journal of Clinical Neurology.